Neuroplastogens
What is a Neuroplastogen?
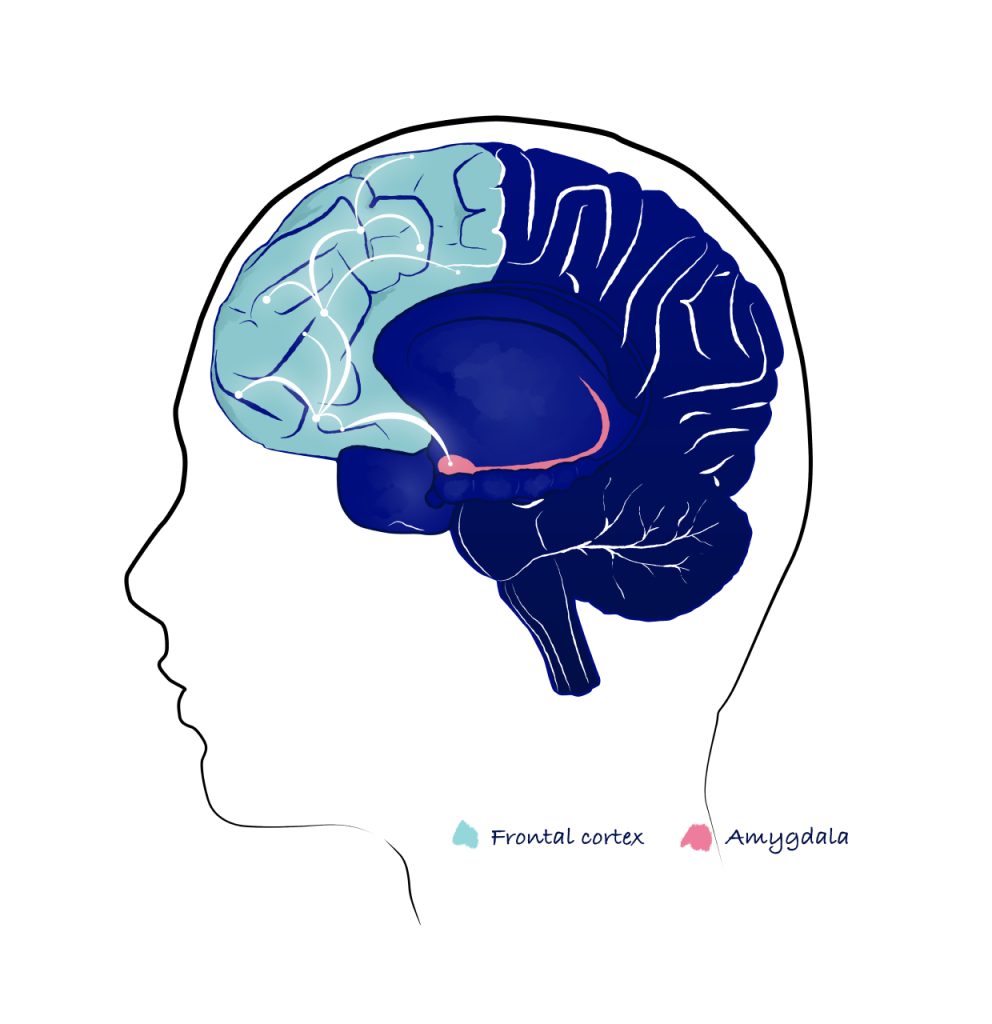
Neuroplastogens are agents that enhance neuroplasticity and hold therapeutic potential to treat many central nervous system (CNS) disorders. Neuroplasticity refers to changes in the structure, connectivity and function of brain cells. It is how the brain adapts to new learning and experiences and is impaired by CNS disorders including PTSD, depression and anxiety. Rapidly acting neuroplastogens induce rapid, robust, and long-lasting improvement in neuroplasticity and behavior, corresponding to fast-acting, meaningful and durable clinical benefit.